CoinJoin: What Is It and How It Works
Explore CoinJoin, a privacy technique used in Bitcoin transactions. By combining transactions, CoinJoin enhances anonymity, protecting your financial privacy. Learn about its benefits and how it works
What Is CoinJoin?
CoinJoin is a decentralized coin mixing protocol for Bitcoin and other compatible cryptocurrencies. It's designed to enhance privacy and anonymity, by basically breaking the links of the past history of your coins. CoinJoin is gaining popularity among users who seek to anonymize their funds, especially those acquired from KYC exchanges or for other various purposes.

Introduced by former Bitcoin developer Gregory Maxwell in 2013, it aims to address the issue of pseudo-anonymity in Bitcoin transactions, which can be traced on the blockchain.
The protocol works by combining multiple transactions into a single pool, making it difficult for third parties to identify the sources and destinations of funds. Participants agree to unite their transactions, and each user retains control over their inputs and outputs through cryptographic signatures.
CoinJoin utilizes Bitcoin UTXOs to create a large pool of currencies, ensuring a higher level of anonymity. However, it is essential to note that CoinJoin does not guarantee complete anonymity, as sophisticated tracking and analysis methods can still uncover user identities.
Implementations like Samourai Wallet, Wasabi Wallet, and JoinMarket facilitate CoinJoin transactions, offering users better privacy options. Although the protocol enhances privacy, it also increases transaction costs due to additional mixing hops.
The future of privacy in Bitcoin lies in providing users with options for varying degrees of anonymity without imposing it by default. Confidential transactions and soft forks are among the developments aimed at improving privacy on the network.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| 💰 CoinJoin | A privacy-enhancing technique in Bitcoin where multiple users combine their transactions to obfuscate the link between inputs and outputs. |
| 💼 UTXO | Unspent Transaction Output; a representation of unspent Bitcoin received in previous transactions. |
| 🔄 Mixing | The process of combining and shuffling multiple transactions to make it harder to trace individual coins. |
| 📄 Transaction | A record of value exchange on the Bitcoin blockchain, consisting of inputs, outputs, and digital signatures. |
| 🔒 Privacy | The state of being unobserved or undisclosed, protecting sensitive information from public view. |
Prerequisites To Understand CoinJoin

To fully understand how CoinJoin works, it is essential to understand Bitcoin transactions and UTXOs (unspent transaction outputs). If you already know about this topic, you can skip this part.
Bitcoin Transactions
Bitcoin transactions consist of inputs and outputs, containing bitcoin amounts, along with digital signatures made using private keys. Analogous to a bank check, a transaction specifies the sender's account, the recipient, the amount, and a signature.
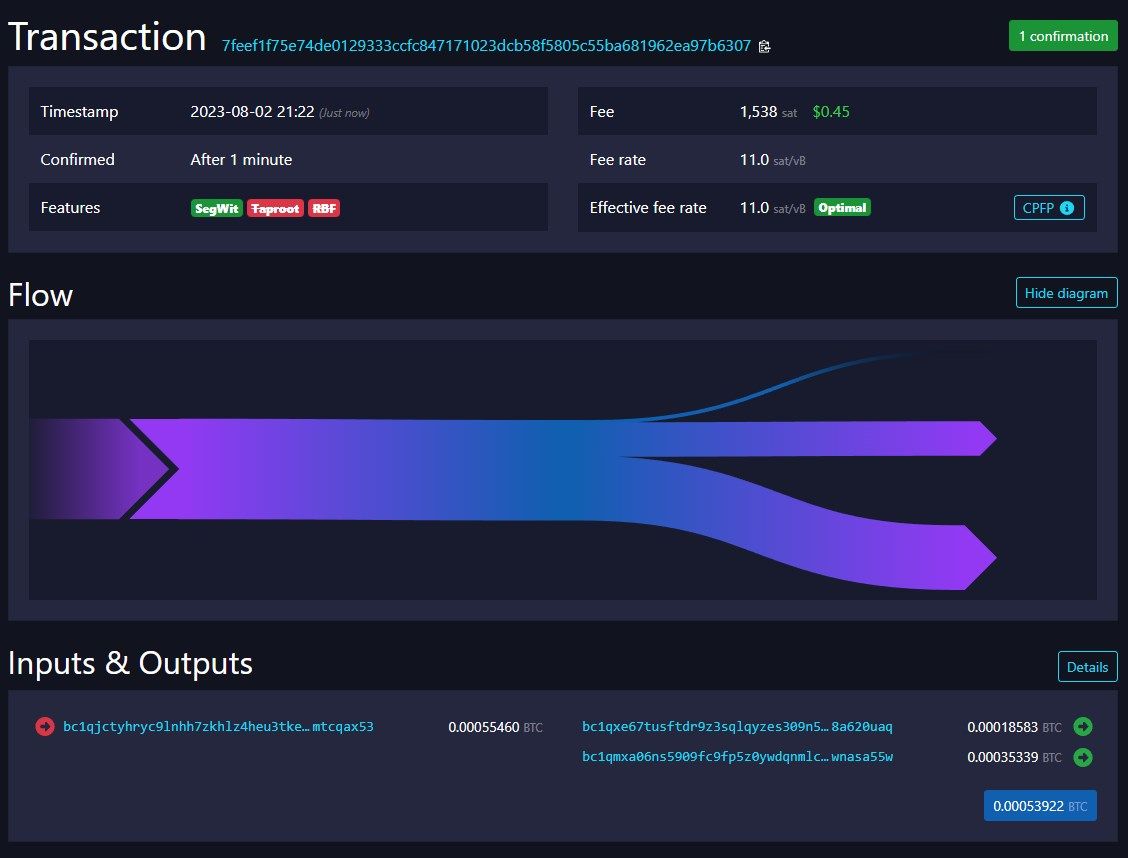
In the provided screenshot, you can observe a random Bitcoin transaction extracted from the Mempool.Space website. Bitcoin transactions are transparent on the blockchain and can be freely accessed online.
On the left column, there is one input and two outputs on the right, along with an additional fee paid to the Bitcoin network. The total value of the inputs is nearly equal to that of the outputs, with a slight variation due to fees, which are collected by the block miner.
In the top right corner, the fee calculation shows 1538 satoshis, equivalent to approximately $0.45 USD at the time of writing.
UTXO
UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) is a term that describes the received coins in a Bitcoin wallet. It is better to think of bitcoin amounts as discrete units, similar to coins in a bag. For example, if you receive 1.5 bitcoins to your wallet, you have a 1.5 bitcoin UTXO. To spend a portion of it, you can't divide it directly but must create a transaction. In the transaction, you can split the amount as needed and send it to various addresses, including back to your own.
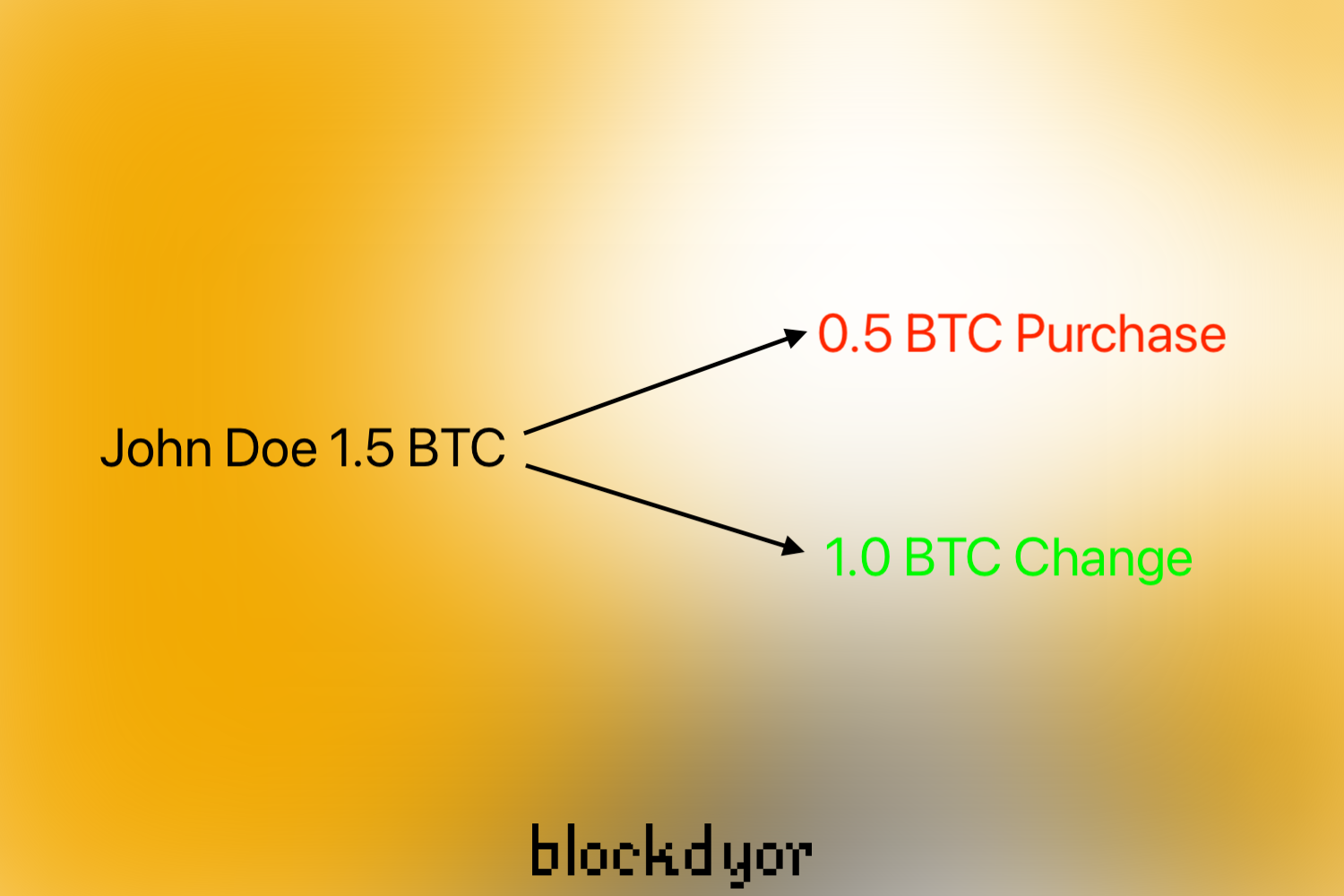
The concept of "change" comes into play when spending a fraction of the UTXO. For instance, if you need to pay 0.5 bitcoins for some kind of purchase, you would use the 1.5 bitcoin UTXO as input and create two outputs: 1 bitcoin for the payment and 1.0 bitcoin as change back to your own address.
In another example, if you have UTXOs of 0.3, 0.6, and 0.05 bitcoins and need to pay 0.8 bitcoins, you would combine the 0.3 and 0.6 bitcoin UTXOs in a transaction. The output would be 0.8 bitcoins for the payment and 0.1 bitcoin as change. After the transaction, your wallet would have two UTXOs, totaling 0.105 bitcoins (excluding mining fees).
How CoinJoin Works
CoinJoin operates on the principle that a single transaction can contain digital signatures from multiple individuals, enabling a unique privacy feature. When two or more people participate in a CoinJoin, their transactions are merged into one, making it challenging to ascertain the ownership of specific coins after the process. This ambiguity is achieved by aligning the sizes of inputs or outputs, ensuring transaction data conceals individual ownership effectively.
The typical pseudonymous property of Bitcoin allows coins to be traced as they are spent, providing some insight into the identity of the users. For instance, if a coin moves from address A to address B and then to address C, it might be possible to infer that the coins in address C belong to the individual who owned address A. However, when customers of exchanges undergo the Know Your Customer (KYC) process, and coins are withdrawn from the exchange and sent to an address, a real identity is linked to the transaction.
Surveillance companies and entities with access to the exchange's KYC data can now associate a coin with a specific individual. It is essential to note that the blockchain itself does not contain identification information; this data is external to Bitcoin. The true identity of coin owners can only be determined by those with access to the exchange's KYC data, which includes the exchange itself, surveillance companies, governments, or hackers.
CoinJoin is a technique that disrupts the pseudonymous identification link from Address A to B to C in Bitcoin transactions, ensuring increased privacy and anonymity. The process involves combining multiple transactions into a single one, making it challenging for observers to determine the true ownership of specific coins.
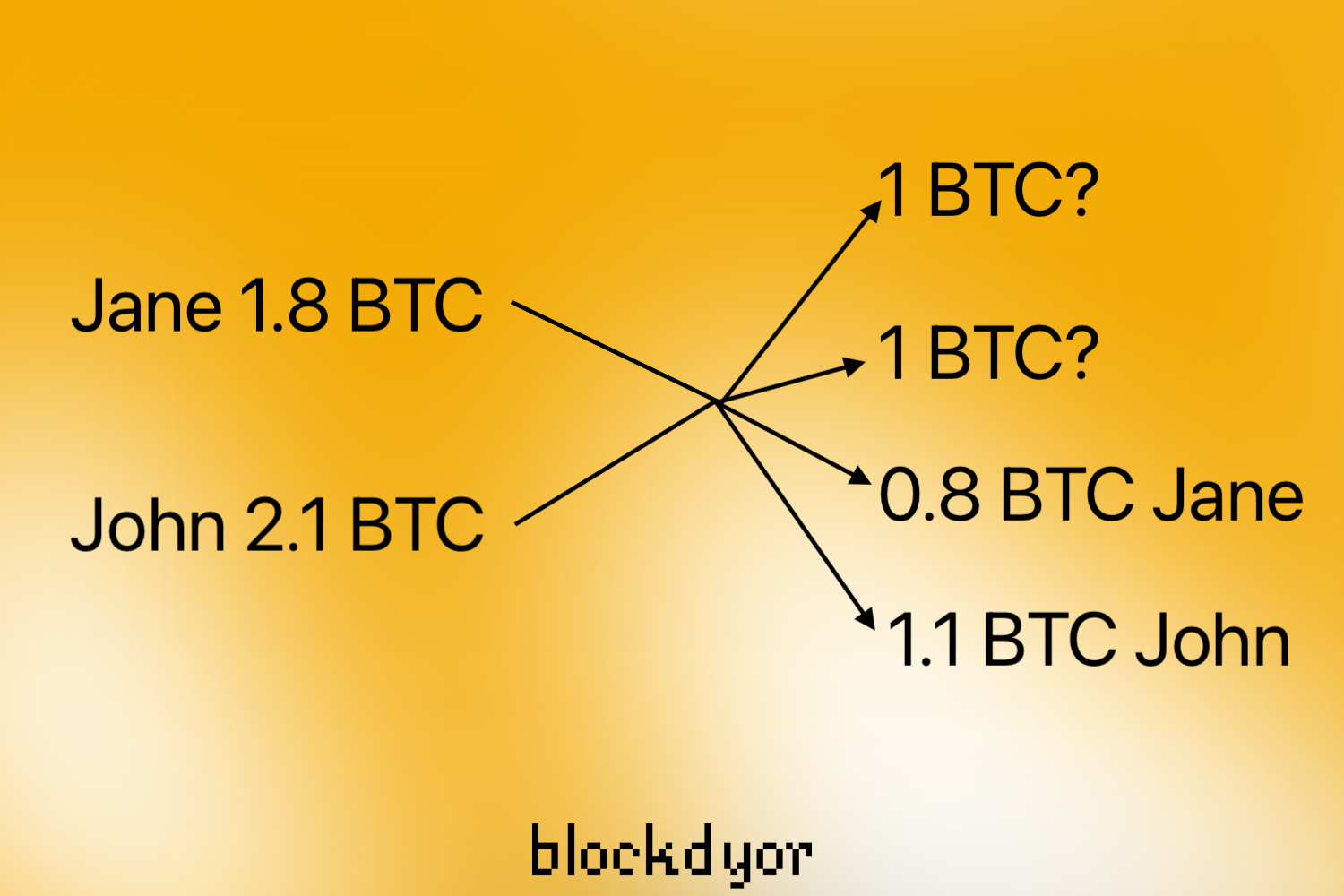
Imagine a scenario where two individuals, Jane and John, each have their respective inputs in a transaction. However, for outsiders without access to KYC data, they are simply known as Person A and Person B, maintaining their anonymity.
In a CoinJoin example, two UTXOs with identical values, say 1.0 bitcoin each, are created. The key idea here is that it becomes unclear which UTXO belongs to Jane (Person A) and which one belongs to John (Person B). Both UTXOs carry a 50% chance of being owned by either Jane or John. As a result, deducing the ownership of individual UTXOs, like the 0.8 and 1.1 bitcoin amounts, becomes challenging due to the mixing process.
Let's consider Alice, who receives 1.0 bitcoin into one of her wallet addresses. For an external observer, the ownership of that 1.0 bitcoin is only 50% certain since it could belong to either Alice or another unknown person. To bolster her privacy, Alice can further mix these coins with someone else. However, it is crucial to avoid mixing with Bob, as they were both part of the initial CoinJoin, and re-mixing together would compromise their privacy.
What CoinJoin Can Do For You?
CoinJoin offers a powerful solution to enhance the privacy and control over your Bitcoins, especially those acquired through various sources like the KYC exchanges. By using CoinJoin, everybody can anonymize their Bitcoin transactions, ensuring that sensitive data associated with them remains confidential.
As we have seen, the process involves mixing the Bitcoins with those of others, making it challenging for anyone to trace back the origins of individual coins. This way, we can retain complete control over our Bitcoins, and only we decide who gains access to our transaction data. It grants us the freedom to release information only to trusted parties while safeguarding our utmost privacy.
It is essential to understand that privacy doesn't necessarily mean not paying taxes, but instead giving information solely to those we trust, and CoinJoining facilitates exactly that. It allows us to dissociate our Bitcoins from their original sources, empowering us to keep our financial activities private from unwanted scrutiny.
Now, to delve into practicality, let's conduct a comprehensive review of the steps involved. By following this procedure diligently, we can confidently take charge of our data and retain the power to decide how we wish to manage our Bitcoin holdings.
Hide The Bitcoins From The Government
Coinjoining, despite its benefits in obfuscating transaction details, does not shield the size of your KYC (Know Your Customer) bitcoin holdings from the government or tax authorities. When you acquire bitcoins through an exchange that follows KYC regulations, you have already disclosed your identity by submitting relevant identification documents. Consequently, the government can access information about your transactions and withdrawals if required.
Even if you proceed to withdraw the purchased bitcoins to your personal wallet and later engage in CoinJoining to increase privacy, it does not erase the fact that you own a specific amount of bitcoin. The government will still be aware that you possess, for example, 1 bitcoin. While they may not know the exact addresses of your bitcoins after CoinJoining, they possess knowledge of your overall bitcoin ownership.
In scenarios where you choose to sell your bitcoin, it is generally mandatory to report the sale according to the law. Furthermore, if legislation is passed to seize bitcoin assets or tax unrealized gains, the government will have accurate insights into the total amount of bitcoin you own.
Remember, CoinJoining is a privacy-enhancing technique that focuses on obscuring the traceability of individual bitcoin transactions. However, it does not erase the initial disclosure of bitcoin ownership through KYC procedures, and relevant authorities can still access this information if necessary.
Boating Accident
If you decide to claim that you lost all your bitcoin in a boating accident, there is a crucial consideration to keep in mind. The coins that were previously associated with your identity, before the supposed accident, must remain untouched and inactive. If these coins are ever spent or moved after the accident, it could expose your claim of the boating mishap as fraudulent.
While mixing your coins using CoinJoin before the accident might add an additional layer of obscurity, I must emphasize that I am not suggesting this strategy. Mixing coins can be risky, and it's essential to exercise caution when employing such techniques.
So, if you genuinely wish to use the boating accident narrative to explain the disappearance of your bitcoin, it is imperative that the coins previously linked to your identity remain dormant and untouched. Any movement of those coins after the accident could cast doubt on the validity of your claim, potentially revealing it as a fraudulent attempt. It's essential to approach such situations with honesty and responsibility.
Protect your privacy
Using CoinJoin can significantly enhance your privacy when transacting with bitcoin. When you spend bitcoin after mixing your coins, the recipient won't have a clear record of where that payment originated. Let me elaborate on this:
Suppose you possess 10 bitcoin in a single address, and you use a portion of it, let's say 0.05 bitcoin, to pay someone. Without CoinJoin, the recipient can easily trace back the transaction on the blockchain and see that it came from an address holding 10 bitcoins. This could potentially compromise your privacy and reveal the total amount you hold.
However, with CoinJoin, the situation changes. The payment to the recipient will come from an address that holds a much smaller amount, rather than the 10 bitcoins in your original address. As a result, the recipient won't be able to ascertain the total balance you have in your wallet or the history of that smaller amount. This increased level of privacy ensures that your other coins and their respective addresses remain undisclosed and protected from prying eyes.
Is CoinJoin Worth It?
If you are thinking if CoinJoin is the right choice for you, consider your specific privacy needs and goals. It's important to understand that CoinJoining won't enable you to hide your total bitcoin holdings from the government. However, if your primary concern is spending privacy, CoinJoin can be a valuable tool to achieve it.
Before making a decision, it's worth noting that using the Lightning Network for spending can provide sufficient privacy for most users. The Lightning Network offers an added layer of privacy when conducting transactions.
Nevertheless, if a substantial number of users adopt CoinJoin or if it becomes a default feature in wallets, it can enhance privacy for everyone, even those who don't actively use CoinJoin.
Some individuals express concerns about the possibility of mixed bitcoins being "flagged" and subsequently rejected by exchanges. While this might be a potential issue, it can be easily addressed. One way to mitigate this risk is to use the mixed coins to open Lightning channels. In doing so, recipients of Lightning transactions won't be able to trace the origin of the funds.
Moreover, if you're cautious about fully mixing all your coins, you can opt to mix only a portion of them as a precautionary measure.
How To CoinJoin
Are you considering CoinJoin? Wondering how to get started? Let's explore some popular automatic CoinJoin implementations: Whirlpool, Wasabi, and JoinMarket. Later, we will also have a look at an automatic mode for Coinjoining bitcoin using Electrum.

Automatic CoinJoin
- Whirlpool: Whirlpool is an automated privacy-focused CoinJoin implementation developed by Samourai Wallet. It allows users to mix their bitcoins with others to enhance transaction privacy. The process involves creating "cycles" where multiple participants combine their transactions, making it difficult for external observers to trace the source of individual coins. Whirlpool operates on the principle of trustlessness, ensuring that no single party can control or compromise the mixing process.
- Wasabi: Wasabi is another popular automatic CoinJoin solution that emphasizes privacy and security. Developed by zkSNACKs, Wasabi utilizes a Chaumian CoinJoin protocol, where participants' coins are mixed without any link to their original source. This ensures that the transaction history remains obscured, providing a higher level of privacy. Wasabi Wallet also supports CoinJoin in combination with the Coin Control feature, allowing users to select specific UTXOs for mixing. One-click Wasabi CoinJoin feature has been recently introduced also in hardware wallets, such as the Trezor Model T.
- JoinMarket: JoinMarket is a decentralized CoinJoin platform that facilitates CoinJoin transactions by connecting "makers" (users providing liquidity) with "takers" (users wanting to mix their coins). This approach enhances privacy by avoiding centralized mixing services. JoinMarket enables users to earn fees by acting as makers, further incentivizing the mixing process. While it requires a more technical setup compared to Whirlpool and Wasabi, JoinMarket offers a robust and community-driven CoinJoin solution.
Manual CoinJoin
Considering manual CoinJoin? It has the upside of higher control and cost savings, but there are important factors to consider before proceeding.
Firstly, manual CoinJoin requires doing it in tandem with other participants, which may limit the volume of CoinJoins you can perform. Additionally, you must have knowledge about generating CoinJoin transactions and be confident in fully controlling the process to ensure privacy.
Understanding transaction privacy is crucial, as a mistake during the process could undermine all your efforts. If you are up for exploring the fascinating possibilities of manual CoinJoin, follow these steps:
- Run Your Own Node: Ensure privacy by running your own node. Public nodes might compromise the privacy of mixed coins. Options like Umbrel are beginner-friendly.
- Create a Private Wallet: Use a hardware wallet to create a new private key. Be cautious with Ledger; create a seed before connecting to Ledger Live. Alternatively, use Coldcard for secure wallet creation.
- Find a CoinJoin Partner: Collaborate with others interested in CoinJoining. Expand your network of Bitcoin friends and enhance CoinJoin skills for better opportunities.
- Plan the CoinJoin: Determine UTXOs to use, destination address, mixed coin size, change output, and mining fee. For instance, you could spend a 0.132 bitcoin UTXO as a 0.01 bitcoin mixed coin and 0.122 bitcoin change output.
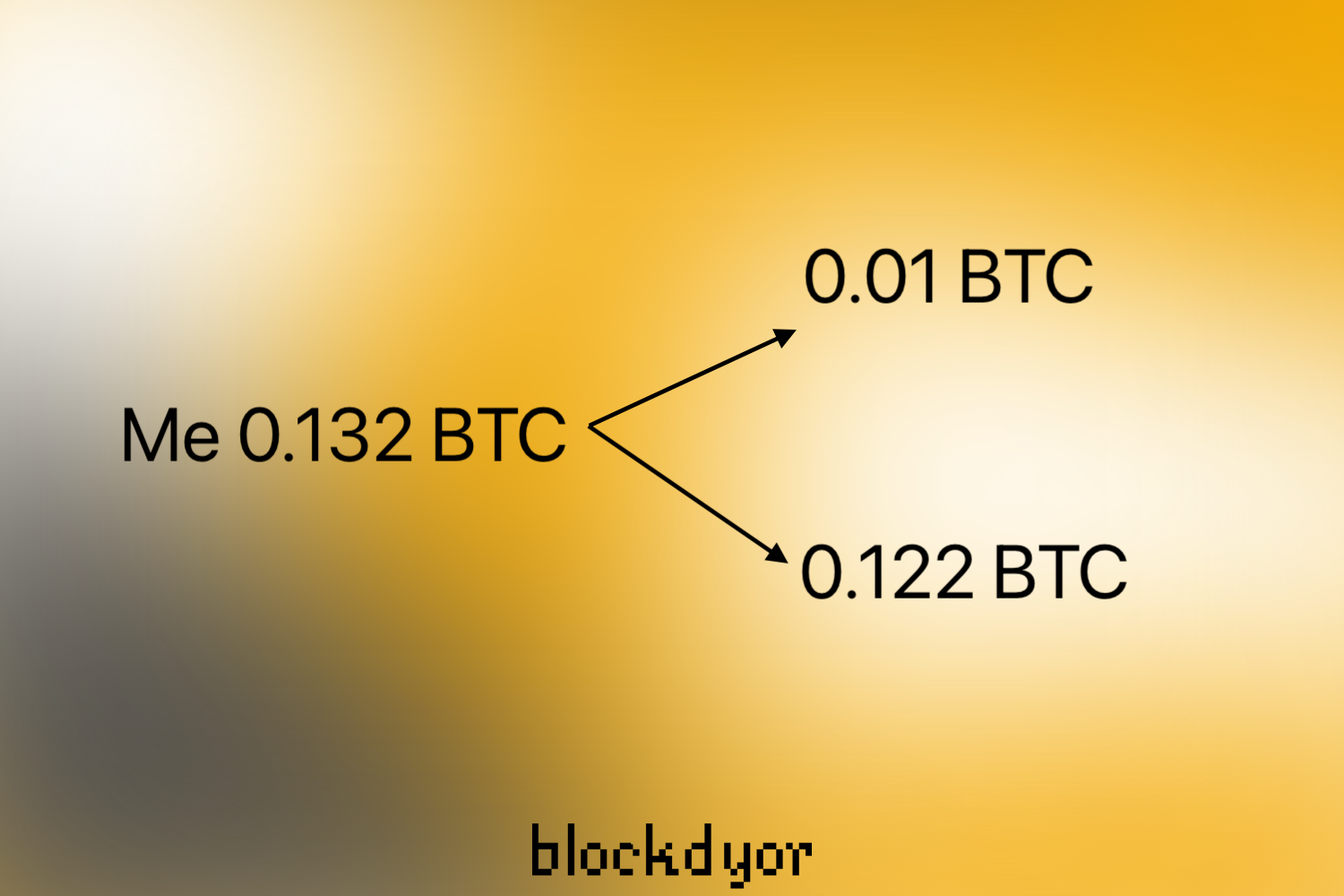
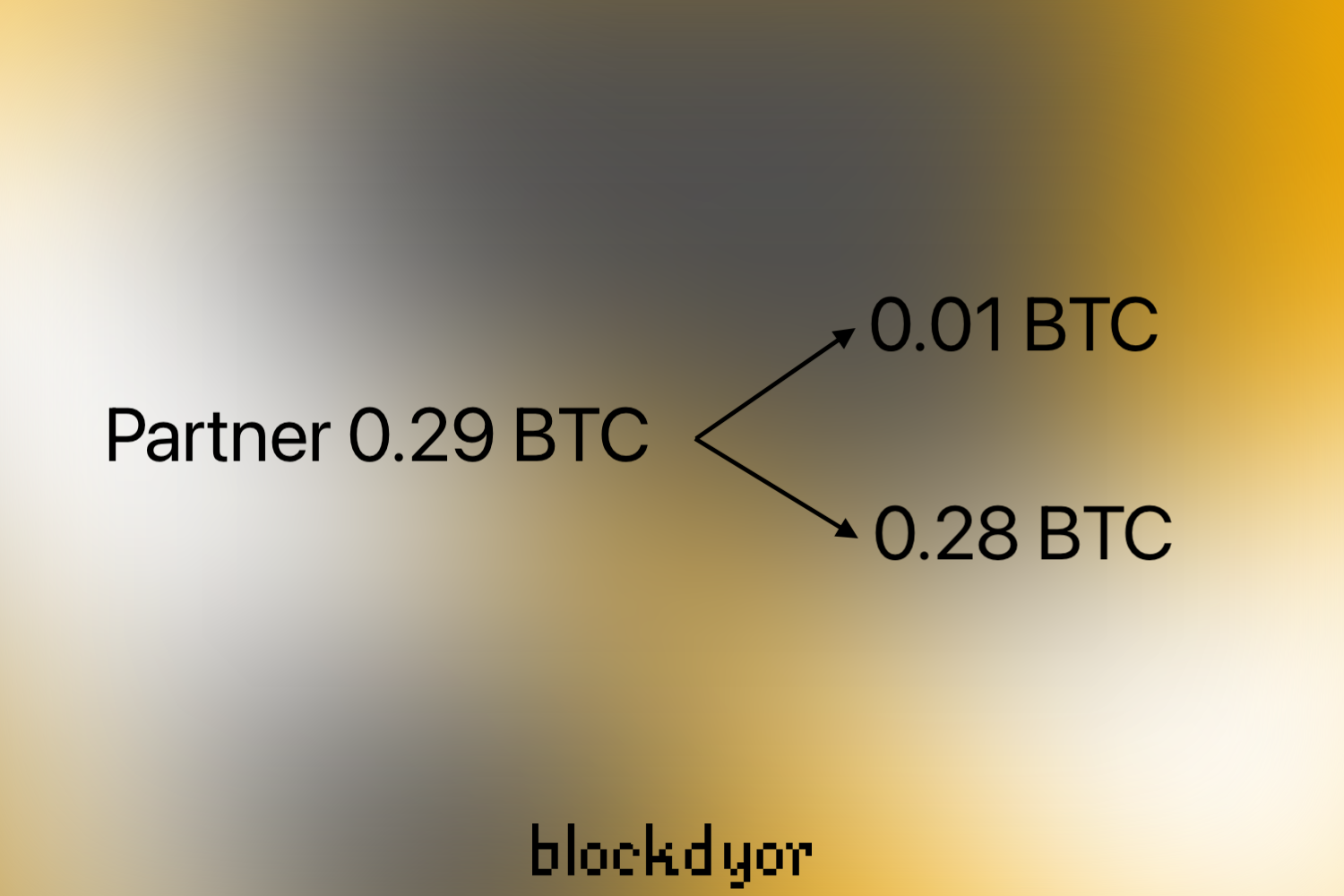
You can then coordinate with your Coinjoin partner to spend a UTXO and create an identical 0.01 Bitcoin mixed output.
- Generate and Save Transaction: Choose UTXO, right-click, "Spend from." Enter destination, pay, finalize, and export the transaction.
- Caution in Sharing: Sharing unsigned transactions risks wallet exposure. Collaborate only with trusted CoinJoin partners.
- CoinJoin Partner's Transaction: Partner sends saved transaction to CoinJoin coordinator. Use secure channels like ProtonMail or explore encryption methods.
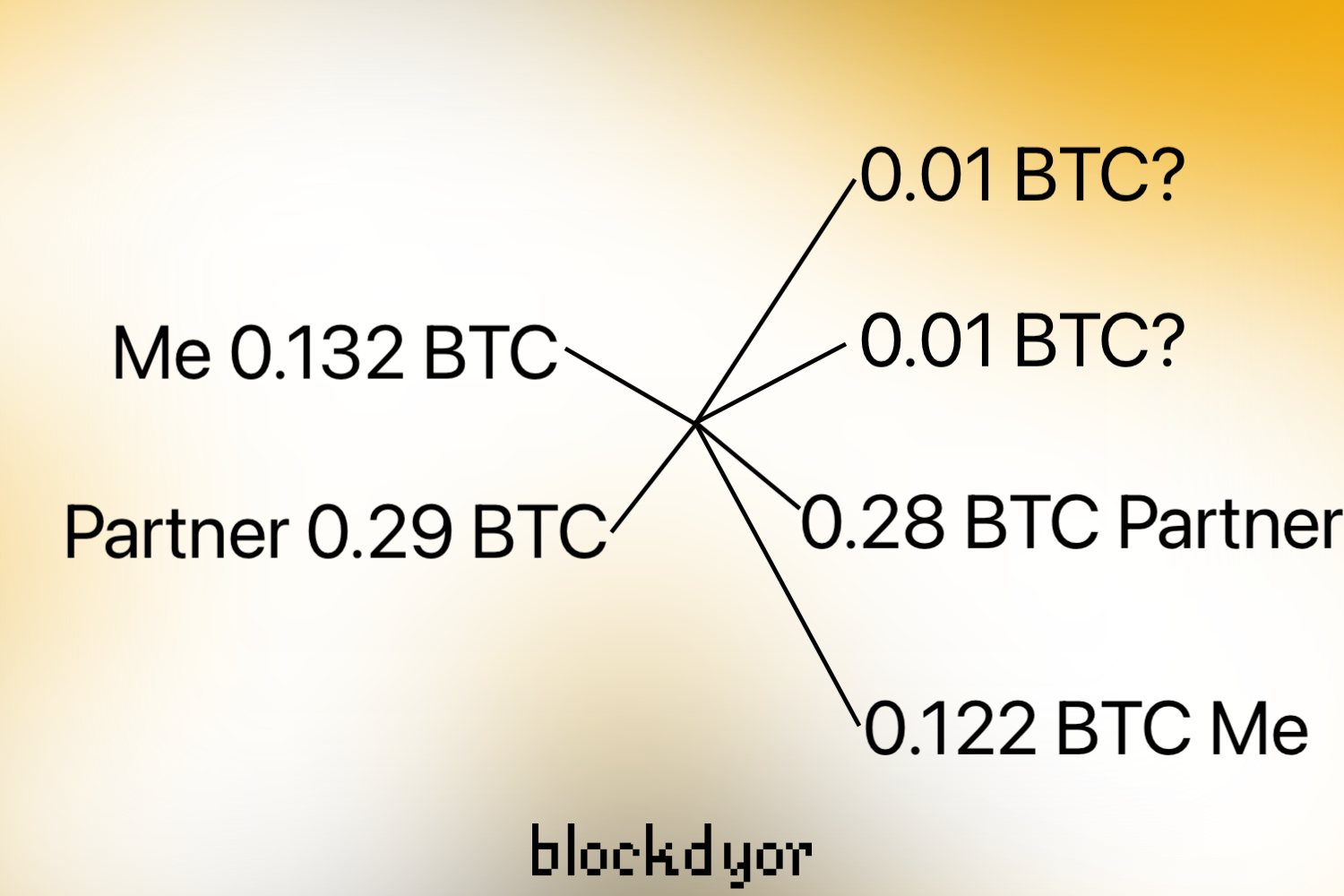
- Merging Transactions: Receive unsigned transactions, save, and open in Electrum. Click "Combine" and "<Join inputs/outputs>" to create a combined transaction.
- Privacy and Recognition: Electrum recognizes its addresses, highlighting them as green (receiving) and yellow (change). CoinJoin transaction includes inputs and outputs from all partners, ensuring privacy.
- Signing Process: All CoinJoin partners sign for validity. Final signer has broadcasting power. Partners decide the order of signing and broadcasting.
- Final Broadcast: Once all signatures are collected, load the transaction, sign, and click "Broadcast" to complete CoinJoin.
Coinjoin Alternatives
When it comes to anonymizing Bitcoin, the options for mixing are rather limited. Let's delve into the primary alternatives available in this domain.
Lightning Network
Another avenue to enhance Bitcoin privacy is utilizing the Lightning Network (LN). Unlike traditional on-chain transactions, LN offers increased privacy due to its particular characteristics. Here's a summarized walkthrough of how it works:
- Convert BTC to Lightning: Suppose you've received 0.5 BTC to your address and wish to anonymize them using a decentralized approach. You can transition these BTC to the Lightning Network, which involves using applications that handle the process automatically.
- Achieve Anonymous BTC: Once your BTC is on LN, it's no longer directly on the blockchain. Instead, it's locked into a contract for use within the Lightning Network. LN transactions provide greater privacy, lower costs, and faster speeds compared to on-chain transactions.
- Transfer BTC Between LN Apps: To avoid revealing the origin of your BTC, you'll move the BTC within LN from one application to another, both utilizing LN extensions. Since these apps don't share user data or communicate, your BTC becomes anonymous in the second application.
- Return to On-Chain: The final step involves moving the anonymous BTC back to an on-chain address, thus completing the process and ensuring enhanced privacy.
While this approach offers speed and privacy benefits, it's essential to weigh the potential fees and complexities against alternatives like using tools such as Whirlpool or Wasabi for achieving anonymity. Nonetheless, being aware of the Lightning Network's privacy potential adds another dimension to your options.
LN + XMR Swaps
Many Bitcoin users opt to leverage Monero (XMR) as a utility coin to enhance privacy within the Bitcoin ecosystem. One approach involves the following steps:
- Onchain to Lightning: Transfer your Bitcoin to the Lightning Network for increased transaction privacy.
- LN to XMR Swap: Exchange Lightning Network Bitcoin for Monero (XMR) to further enhance privacy.
- XMR Transaction: Conduct a confidential Monero transaction to maintain privacy.
- XMR to LN to BTC: Convert Monero back to Bitcoin via the Lightning Network.
In the past, we explored cross-chain swap solutions like Sideshift, which offers effective integration with Bitcoin for seamless transactions.
Pros & Cons of Coinjoin
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Enhances transaction privacy | ❌ Coordination with others may limit volume |
| ✅ Protects sender's and recipient's privacy | ❌ Requires understanding of transaction privacy |
| ✅ Can break pseudonymous identification links | ❌ Possibility of making errors during setup |
| ✅ Increases overall privacy when widely adopted | ❌ Potential exposure of addresses to random nodes |
| ✅ Can be used to improve privacy in Lightning Network payments | ❌ Transaction history must be managed carefully |
| ❌ Manual CoinJoining can be complex and risky | |
| ❌ May have limited impact if not widely adopted | |
| ❌ Some people who do coinjoins are the ones with tainted coins | |
| ❌ Requires running and managing your own node |
Bottom Line
In the dynamic realm of cryptocurrency, CoinJoin it's still probably the best solution to increase privacy, enabling users to safeguard their financial information from prying eyes. By severing the link between addresses and introducing transactional uncertainty, CoinJoin provides a valuable shield against surveillance. However, potential challenges, such as coordination complexities and manual intervention, warrant thorough consideration.
Moreover, the advent of the Lightning Network brings forth an intriguing alternative for "anonymizing" your Bitcoin. This innovation, which ensures quicker and more confidential transactions, arguably lessens the immediate necessity for CoinJoin, as it accomplishes similar privacy goals.
As the cryptocurrency community continues to evolve and increase in adoption, the decision to use CoinJoin or explore other privacy-enhancing avenues must be made with a keen awareness of both the advantages and potential pitfalls. The road to heightened financial privacy is not without its complexities, but with informed choices, users can navigate the evolving landscape and embrace tools that empower them to take charge of their digital financial interactions.