Bitcoin Mining: What Is It And How Does It Work?
Bitcoin mining involves solving complex mathematical problems to verify transactions and create new bitcoins. This guide explores the fundamentals of the process, from hardware requirements to the economics behind it.
Bitcoin mining is a complex process through which new bitcoins are introduced into circulation, as well as how the network validates new transactions, and sustains the maintenance and evolution of the blockchain ledger.
In the mining process, sophisticated hardware is utilized to engage in a computationally intensive task. Miners engage in a race to find a specific number through a trial-and-error approach combined with hashing. The first miner to successfully find this number is rewarded with the next block of bitcoins, and the cycle continues.
However, it's crucial to note that this rewarding process occurs primarily during the network's initial phase. Currently, we are still in this initial phase, and mining remains a pivotal component of securing and validating transactions within the Bitcoin network.
While cryptocurrency mining can be extremely expensive, and only sporadically lucrative, it still have interest for many crypto firms and investors. This is likely due to the fact that miners gets awarded with bitcoin as a reward for their processing power.
The incentive of receiving a bitcoin reward is what drives miners to assist with the primary objective of mining: to validate and monitor Bitcoin transactions, ensuring their legitimacy. Due to this shared responsibility among numerous users worldwide, Bitcoin is considered a "decentralized" cryptocurrency that doesn't depend on any central authority, such as a central bank or government, for regulatory oversight.
Nevertheless, before investing in the necessary equipment and time, it's crucial to read this guide to determine whether mining is truly right for you, and why it's so important for the network's security.
| TERM | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| 🔒 Hash rate | The speed at which a miner can perform the computational tasks necessary to validate transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain |
| 🧐 Mining difficulty | The measure of how hard it is to mine a new block on the Bitcoin network, adjusted every 2016 blocks |
| 💻 ASIC | Short for "application-specific integrated circuit," a type of computer chip designed specifically for Bitcoin mining |
| 👥 Pool mining | A collaborative approach to mining in which miners combine their computing power to increase their chances of solving the equations and earning rewards |
| 🪙 Halving | A reduction in the reward given to Bitcoin miners for adding new blocks to the blockchain, occurring approximately every four years |
| 💰 Reward | The amount of Bitcoin given to a miner for successfully validating transactions and adding a new block to the blockchain |
| 💸 Block subsidy | The portion of the block reward that is paid out to miners, currently 6.25 BTC |
| 📈 Transaction fees | The additional fees paid by users for their transactions to be included in a block, currently making up a significant portion of miner revenue |
Understanding the Basics of Bitcoin Mining

Bitcoin mining is the process of adding new transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain by doing energy-intensive computational tasks. Miners use specialized computer equipment to solve these problems and validate transactions, and in return, they are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins.
Bitcoin mining is a critical part of the Bitcoin ecosystem. Mining ensures that the Bitcoin network remains secure and trustworthy, as miners execute computational tasks to validate transactions. This competition makes it very difficult for any one person or group to manipulate the network or double-spend their Bitcoins.
Bitcoin mining is a profitable business for those who invest in the right equipment and have access to cheap electricity. Bitcoin mining is basically a way for individuals and companies to participate in the Bitcoin network and earn passive income.
Bitcoin mining can help to accelerate the transition to clean energy. By using excess energy from renewable sources to power Bitcoin mining operations, miners can monetize that energy and make it more economically viable to build more renewable energy infrastructure. This, in turn, could help to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
Bitcoin Mining: How Does It Work?
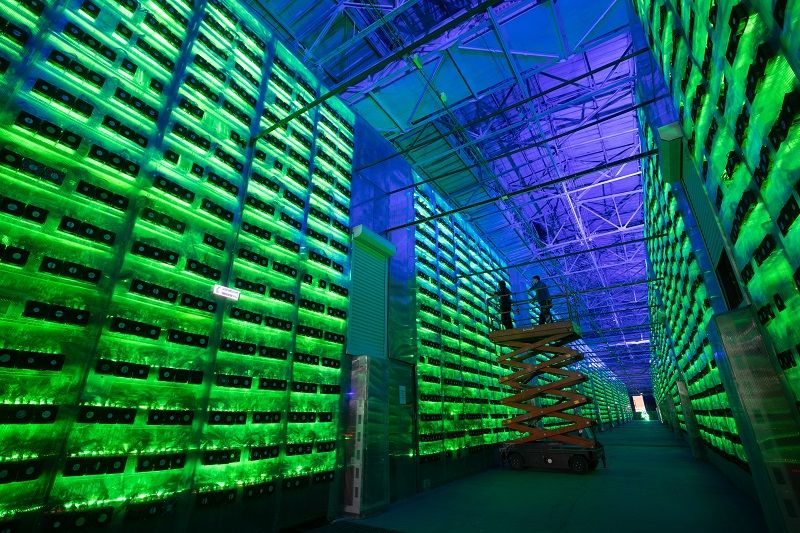

The Bitcoin network is based on a decentralized ledger that is maintained by a network of computers around the world. Miners use specialized software and hardware to solve cryptographic puzzles and validate transactions on the network. The mining process involves verifying transactions and adding them to a block, which is then added to the blockchain. This process is known as "proof of work" and is designed to prevent double-spending and other fraudulent activities.
To mine Bitcoin, miners must first download and install a Bitcoin wallet, which is used to store their earnings. They also need to have access to specialized mining hardware, such as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), which are devices designed specifically for mining Bitcoin.
Once the hardware is set up, miners can connect to the Bitcoin network using an internet connection and establish their mining operations. An ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) is required for efficient mining, and joining a mining pool is recommended for increased chances of earning rewards. The days of solo mining via Bitcoin Core are long gone, as the industry has evolved.
In terms of software, it's important to note that most ASICs come preloaded with CGminer or a forked version of it. This eliminates the need for additional mining software, making the setup process more streamlined. However, it's worth mentioning that certain ASICs, such as Gekkoscience ASICs, cater more to hobbyist or home mining setups rather than large-scale operations.
Overall, while a full node is not necessary for mining, an internet connection, an ASIC, and participation in a mining pool are the primary requirements to engage in Bitcoin mining efficiently in today's landscape.
The first miner to solve the puzzle and add the block to the blockchain is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins, as well as any transaction fees associated with the block. This reward is halved every 210,000 blocks, which means that the supply of new bitcoins is gradually reduced over time.
The Role of Miners in Validating Transactions
Miners play a critical role in validating transactions on the Bitcoin network. Transactions are the backbone of the Bitcoin system, and they enable users to send and receive bitcoins to and from each other.
When a user starts a Bitcoin transaction, it is broadcast to the network and picked up by nodes. These nodes verify the transaction by checking that the sender has enough bitcoins to send and that the transaction adheres to the rules of the network.
Once a transaction is verified by the nodes, it is then bundled together with other transactions into a block. This block is then broadcasted to the network, where miners engage in a process similar to brute-forcing linked to the block.
The first miner to solve the puzzle and add the block to the blockchain is rewarded with newly minted bitcoins, as well as any transaction fees associated with the block. This reward incentivizes miners to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
By validating transactions, miners ensure that the Bitcoin network operates smoothly and that there is no double-spending. Double-spending is the act of spending the same bitcoins twice, and it can be a major problem in digital currencies. By adding transactions to the blockchain, miners create a permanent record of all transactions, which ensures that bitcoins can only be spent once.
In addition to validating transactions, miners also help to secure the network by contributing their computational power to the Bitcoin system. The more miners there are on the network, the more secure it becomes, as it becomes increasingly difficult for any single miner to take control of the system.
Bitcoin Mining Hardware and Software Requirements
Bitcoin mining requires specialized hardware and software to participate in the network and compete for the right to add new blocks to the blockchain. Here are the basic hardware and software requirements for Bitcoin mining:
Hardware requirements:
- ASIC miners: Bitcoin mining requires specialized hardware called ASIC miners (Application Specific Integrated Circuit). These machines are designed specifically for mining Bitcoin and are much more powerful than general-purpose computers. ASIC miners are available from various manufacturers such as Bitmain, Canaan, and MicroBT.
- Power supply: ASIC miners require a lot of power to operate, and you will need a high-quality power supply to keep them running. Make sure to calculate the total power consumption of your miners and buy a power supply that can handle the load.
- Cooling system: ASIC miners generate a lot of heat, and you will need a good cooling system to prevent them from overheating. You can use air or liquid cooling systems, depending on your preference.
- Internet connection: Bitcoin mining requires a stable internet connection with high bandwidth to communicate with the network and receive new blocks.
Software requirements:
- Bitcoin wallet: You will need a Bitcoin wallet to receive and store the rewards from mining. There are various types of wallets available, including hardware wallets, software wallets, and mobile wallets.
- Mining software: You will need mining software to connect your ASIC miners to the Bitcoin network and start mining. There are several popular mining software options, including CGMiner, BFGMiner, and EasyMiner.
- Mining pool: Joining a mining pool can increase your chances of earning rewards by combining your computing power with other miners. There are many mining pools available, and you can choose one based on the pool fees, payout methods, and other factors.
Bitcoin mining requires significant upfront investment in hardware and electricity costs, as well as ongoing maintenance and monitoring of your mining operations.
Pros and Cons of Bitcoin Mining
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Potential profits | ❌ High upfront costs |
| ✅ Decentralized network | ❌ Energy consumption |
| ✅ Flexibility | ❌ Competition |
| ✅ Learning experience | ❌ Technical expertise |
How to Get Started with Bitcoin Mining
Getting started with Bitcoin mining requires a significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and electricity costs. Here are the basic steps to get started with Bitcoin mining:
- Choose your hardware: The first step in Bitcoin mining is to choose your hardware. You will need to invest in specialized mining hardware, such as ASIC miners, to compete with other miners on the network. Research different hardware options, compare prices and specifications, and choose the hardware that best suits your budget and mining goals.
- Set up your mining rig: Once you have your hardware, you will need to set up your mining rig. This involves assembling your hardware, connecting it to a power supply, and installing the necessary software.
- Choose your mining pool: Joining a mining pool can increase your chances of earning rewards by combining your computing power with other miners. Research different mining pools, compare their fees, payout methods, and other factors, and choose the one that best suits your mining goals.
- Download mining software: You will need mining software to connect your mining rig to the Bitcoin network and start mining. There are several popular mining software options available, including CGMiner, BFGMiner, and EasyMiner. Choose the software that best suits your hardware and operating system.
- Create a Bitcoin wallet: You will need a Bitcoin wallet to receive and store the rewards from mining. There are various types of wallets available, including hardware wallets, software wallets, and mobile wallets. Choose the wallet that best suits your security needs and preferences.
- Join a mining pool: Once you have your mining rig set up, mining software installed, and Bitcoin wallet ready, you can join a mining pool and start mining. Your mining pool will provide you with instructions on how to connect to their pool and start mining.
- Monitor your mining operations: Bitcoin mining requires ongoing maintenance and monitoring of your mining operations. Keep an eye on your hardware's temperature and power consumption, and adjust your mining settings as needed to optimize your performance and profits.
Getting started with Bitcoin mining can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it can also be a rewarding and profitable activity. Make sure to do your research, calculate your costs, and choose the hardware, software, and mining pool that best suits your mining goals and budget.
Challenges and Risks Associated with Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining can be a profitable and exciting activity, but it also comes with several challenges and risks that miners should be aware of. Here are some of the main challenges and risks associated with Bitcoin mining:
- High energy consumption: Bitcoin mining requires a significant amount of energy, and this has led to criticism over its environmental impact. Miners need to factor in the cost of electricity when calculating their profits, and they should consider using renewable energy sources where possible.
- Competition: As the Bitcoin network has grown, mining has become increasingly competitive. Individual miners may find it difficult to compete with larger mining operations, and it can be challenging to earn a profit from mining.
- Hardware costs: Bitcoin mining requires specialized hardware, such as ASIC miners, which can be expensive. The cost of hardware can be a significant upfront investment for miners, and it can be challenging to recoup these costs.
- Technical expertise: Bitcoin mining requires technical expertise and knowledge of mining hardware, software, and network protocols. Beginners may find it challenging to get started with Bitcoin mining and may need to spend time learning the necessary skills.
- Network difficulty: The Bitcoin network adjusts the difficulty of mining to ensure that new blocks are added to the blockchain at a steady rate. This can make it more difficult for miners to earn rewards and may reduce profitability.
- Regulatory risks: Bitcoin mining is still a relatively new industry, and there is uncertainty around how it will be regulated in the future. Miners should be aware of the regulatory risks and ensure that they are complying with any relevant laws and regulations.
- Security risks: Bitcoin mining can also be subject to security risks, such as hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. Miners should take steps to secure their mining operations and protect their Bitcoin wallets and private keys.
Bitcoin mining can be a challenging and risky activity, but it can also be rewarding for those who are willing to invest the time and resources required. Miners should be aware of the challenges and risks and take steps to mitigate them where possible.
The Skull of Satoshi by Greenpeace
In 2023, the unveiling of an art installation named the "Skull of Satoshi" commissioned by Greenpeace, reignited the conversation around the process of Bitcoin mining.
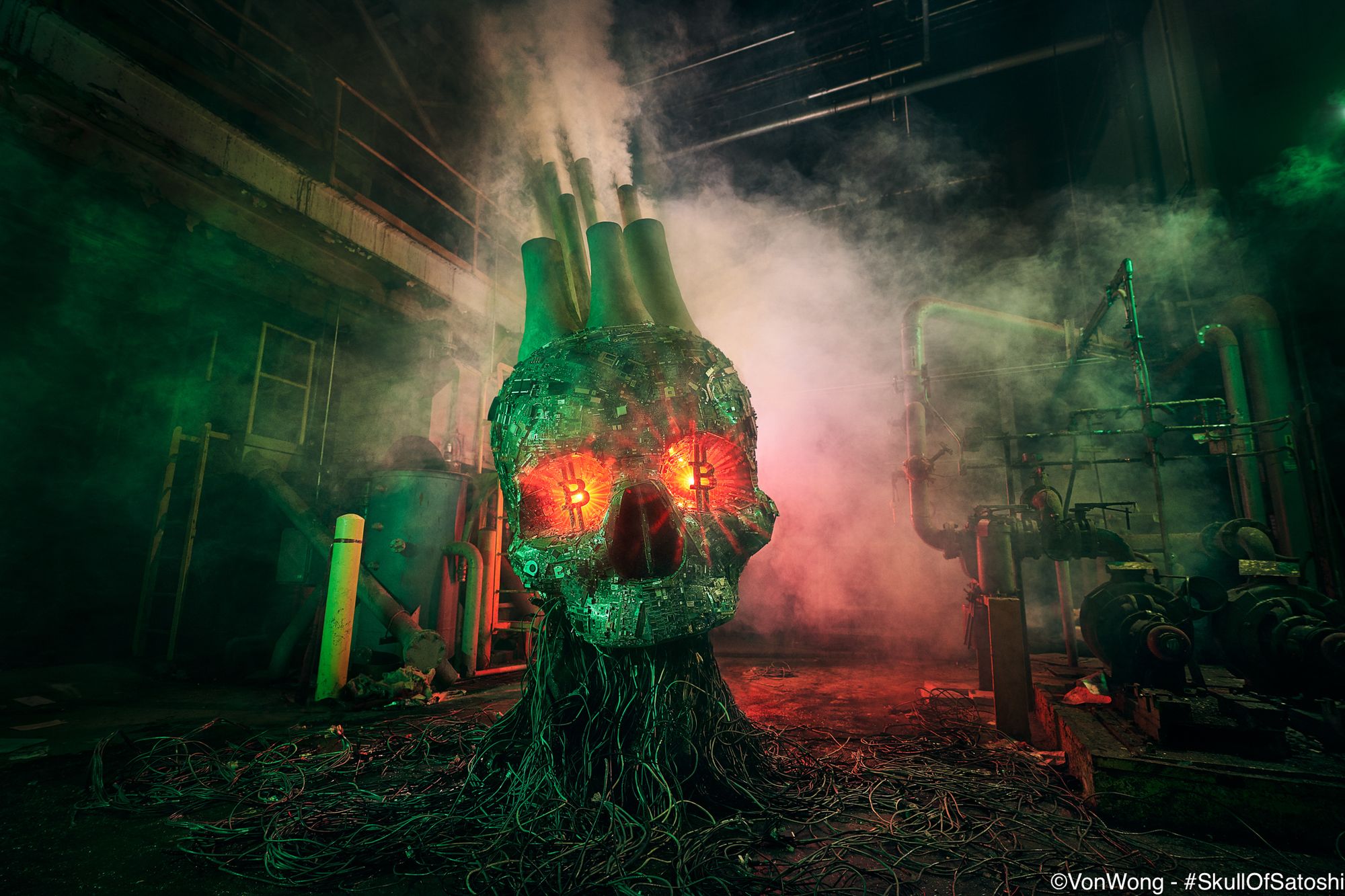

The campaign, which aimed to save the environment by altering Bitcoin's proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm through a "code change," was funded by Ripple co-founder Chris Larsen.
The skull is an impressive 11-foot structure made of recycled styrofoam, wood, and over 300 pieces of electronic waste, with red laser eyes and smokestacks growing out the top. This remarkable piece of art immediately gained popularity in the Bitcoin community, and despite concerns regarding its source of funding, Bitcoin enthusiasts embraced it with enthusiasm. Some even went as far as changing their Twitter profile pictures to images of the Skull of Satoshi.
The story of the Skull of Satoshi is fascinating not only because of the impressive art installation and the controversial issue of Bitcoin's environmental impact but also because it highlights the artist Benjamin Von Wong's personal learning journey.
Initially, he believed the only solution to Bitcoin's environmental problem was to move away from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS). However, after conversations with environmentalist bitcoiners, Von Wong's perspective changed, and he recognized that Bitcoin can be a powerful force in improving the environment.
In fact, the Bitcoin Mining Council's 2022 report reveals that an encouraging 59.5% of the global energy used for bitcoin mining is derived from renewable sources. This signifies a positive step forward, and the trend is set to continue with the increasing number of miners constructing facilities powered by eco-friendly options such as solar, wind, and other green energies.
This transformation is crucial for the Bitcoin community to engage constructively with the environmental question as more people become interested in Bitcoin. The story of the Skull of Satoshi underscores the need for the Bitcoin community to become more diverse, inclusive, and capable of addressing environmental issues in creative and innovative ways.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining and its Implications
The future of Bitcoin mining is uncertain, but there are several potential implications that could affect the cryptocurrency industry and the wider economy. Here are some of the possible scenarios for the future of Bitcoin mining and their implications:
| Trends and Implications | Description |
|---|---|
| 📈 Continued growth | With the increasing interest in mining and the expansion of the Bitcoin network, there may be continued growth in the industry, leading to higher competition and energy consumption. This could also result in further advancements in mining technology. |
| 🍃 Shift to renewable energy | In response to environmental concerns, there may be a shift towards using even more renewable energy sources to power mining operations. This could reduce the carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining and improve the industry's reputation. |
| 🌐 Centralization | There is a risk of larger mining operations dominating the network, reducing decentralization and security, and leading to concerns over mining monopolies. |
| 💂 Government intervention | Governments may start to regulate Bitcoin mining more heavily, potentially making it more difficult for miners to operate, especially in countries with stricter regulations. |
| 🌎 Impact on the wider economy | As Bitcoin mining becomes more mainstream, it could have wider economic implications such as higher energy prices or supply shortages due to increased energy consumption. On the other hand, a shift to renewable energy could lead to new investment opportunities and job creation in the renewable energy sector. |
The future of Bitcoin mining is likely to be influenced by a range of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory developments, and environmental concerns. As the industry continues to evolve, it will be important for miners, investors, and policymakers to keep up with the latest developments and understand the potential implications for the wider economy.
Bottom Line
Bitcoin mining is the process of validating transactions and adding new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain using a specific type of computer hardware and software.
While mining can be profitable and exciting, it also comes with several challenges and risks, such as high energy consumption, competition, hardware costs, technical expertise, network difficulty, regulatory risks, and security risks.
The future of Bitcoin mining is uncertain, and there are several potential scenarios, including continued growth, a shift to more renewable energy, centralization, government intervention, and wider economic implications.