What is Polygon And How Does It Work?
In this guide, we'll analyze Polygon, a rapidly growing Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that offers fast and low-cost transactions, interoperability, and easy-to-use developer tools. We'll explore its use cases, advantages, and potential impact on the blockchain industry.
Polygon, also known by its ticker symbol MATIC, is a versatile cryptocurrency and platform that is based on blockchain networks to interconnect and expand. As "Ethereum's internet of blockchains," Polygon first emerged in 2017 as the Matic Network.
By leveraging the Ethereum blockchain, the Polygon platform facilitates connections among Ethereum-based projects, offering a potent combination of flexibility, scalability, and sovereignty while still retaining the Ethereum blockchain's security, interoperability, and structural benefits.
As an ERC-20 token, MATIC is fully compatible with other Ethereum-based digital currencies. It plays a crucial role in securing and governing the Polygon network, and is also used to pay network transaction fees.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| 🦄 Symbol | MATIC |
| 🪙 Initial Coin Offering (ICO) Price | $0.00045 (April 2019) |
| 🚉 Platform | Polygon (previously known as Matic Network) |
| ⚖️ Consensus | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
| 📈 Total Supply | 10 Billion MATIC |
| 📉 Circulating Supply | 6.6 Billion MATIC (as of 2024-02) |
| ⛽️ Use Case | MATIC is used to pay for transactions, gas fees, and as a governance token in the Polygon ecosystem. |
| 🔥 Token Burn | MATIC uses a token burn mechanism to reduce the total supply over time. |
What is Polygon?
Polygon is an Ethereum scaling platform that decentralizes the process and enables developers to create user-friendly dApps with low transaction costs while ensuring maximum security.
As per the Polygon Lightpaper, it is a framework and a protocol that interconnects various blockchain networks compatible with Ethereum.
The MATIC-powered Polygon platform was created to foster growth and connectivity among Ethereum-compatible blockchains and projects.
In addition to facilitating transactions and securing the network, MATIC tokens are also used to govern the Polygon ecosystem.
To ensure efficient platform operation, Polygon employs a customized proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
Polygon operates through side chains that run alongside the primary blockchain, forming an ecosystem compatible with a variety of blockchains.
Polygon bridges allow for the transfer of Ethereum-based cryptocurrencies to the Polygon network, with the option of returning to the Ethereum blockchain. MATIC, Polygon's cryptocurrency, serves as a governance token, transaction fee payment, and staking component for the network.
Applications built on Polygon operate similarly to those on Ethereum, but with the advantage of better scalability, resulting in faster and more cost-effective transactions.
Migrating to Polygon's network might be a wise move for businesses that rely on Ethereum, as it eliminates the cost barriers associated with transactions.
Brief History of Polygon

Polygon's co-founders are Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun, and Mihailo Bjelic.
In 2017, a project was launched under the name Matic, aimed at resolving Ethereum's scalability issues.
In 2019, Matic's token called MATIC was launched via an IEO on the Binance cryptocurrency exchange.
The project made significant progress in the summer of 2020 with the release of the Matic network, which came at an opportune time as Ethereum's transaction costs surged with the DeFi hype.
Matic's success led to a rebranding in early 2021, and it is now known as Polygon while its currency is still referred to as MATIC.
Polygon has since announced its commitment to providing a scaling solution not just for Ethereum but also for other blockchains.
The platform has since grown to support over 7,000 blockchain-based projects.
How Polygon works
Polygon is a versatile blockchain concentration that provides customizable scaling solutions for blockchains and distributed applications.
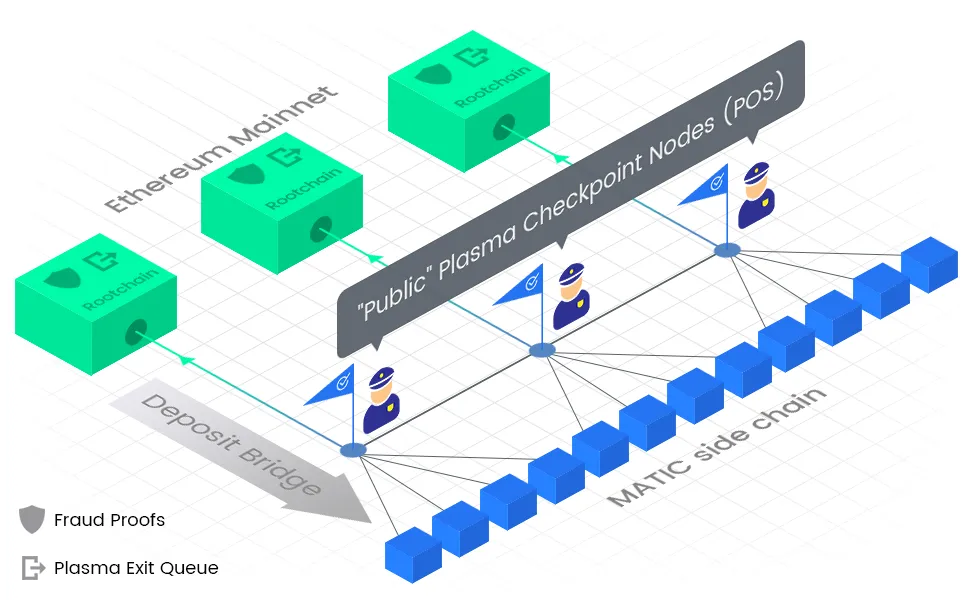
It uses layer 2 solutions and sidechains to handle transactions and ensure security. The ecosystem also includes Plasma, which allows applications to create their own subchains, and Rollup scaling solutions.
Polygon's compatibility with Ethereum Virtual Machine enables easy transfer of smart contracts and applications built on Ethereum to Polygon. With its flexibility and scalability, Polygon is an attractive option for many projects seeking to improve transaction speed and reduce costs.
Polygon Features
Polygon offers a variety of features designed to improve the performance, functionality, and accessibility of decentralized applications (dapps) built on the platform. Here are some of the key features of Polygon.
Scaling Solutions
- Polygon PoS Live: Polygon uses a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm to secure its network and process transactions. This allows for faster transaction processing and lower fees compared to the Ethereum network.
- Polygon Supernodes: Powered by Polygon Edge, this solution allows for higher throughput by using a network of supernodes to process transactions in parallel.
- Polygon Zero Development: A zk-Rollup solution that uses the Plonky2 curve to achieve faster transaction speeds and lower fees.
- Polygon Miden Development: A STARK-based zk-Rollup solution that provides high scalability and privacy for dapps.
- Polygon zkEVM Development: An EVM equivalent zk-Rollup solution that provides the same functionality as the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) but with lower fees and faster transaction times.
Privacy Solutions
- Polygon ID New: A blockchain-native identity system that provides a secure and decentralized way to manage identity information.
Frameworks
- Polygon Edge: A modular and extensible framework for building dapps on Polygon. This framework provides a set of tools and libraries to simplify the development process and offers support for multiple programming languages, including Solidity, Rust, and JavaScript.
Overall, these solutions and frameworks make Polygon an attractive choice for developers looking to build scalable and privacy-focused dapps on the Ethereum network. With a range of tools and infrastructure available, developers can create innovative and efficient solutions that offer the benefits of blockchain technology without the drawbacks of high fees and slow transaction speeds.
Dapps
Polygon has a growing ecosystem of decentralized applications (dapps) that leverage the platform's scaling solutions and infrastructure to provide a range of functionality and services. Here are some examples of popular dapps in the Polygon ecosystem:
- Metamask: Metamask is a popular cryptocurrency wallet and browser extension that enables users to interact with decentralized applications on various blockchain networks, including Polygon. Metamask recently added support for Polygon's PoS network, making it easier for users to access and use dapps built on Polygon.
- PoS Wallet Suite: The PoS Wallet Suite is a set of dapps that provide various functionalities for Polygon's PoS network, including wallet management, transaction processing, and staking. These dapps make it easier for users to manage their Polygon tokens and interact with the network.
- PoS Bridge: The PoS Bridge is a dapp that allows users to transfer assets between the Ethereum network and Polygon's PoS network. This enables users to move tokens between the two networks seamlessly and quickly.
- PoS Staking: PoS Staking is a dapp that enables users to stake their Polygon tokens and earn rewards in return. This dapp incentivizes users to hold and participate in the Polygon network, helping to secure the network and promote its growth.
- PoS Explorer: The PoS Explorer is a dapp that provides real-time monitoring and analytics of the Polygon network, including network statistics, transaction data, and other relevant information.
- Hermez Wallet: Hermez is a decentralized scaling solution that enables high-speed and low-cost transactions on the Ethereum network. The Hermez Wallet is a dapp that allows users to manage their Hermez tokens and interact with the Hermez network.
- Hermez Explorer: The Hermez Explorer is a dapp that provides real-time monitoring and analytics of the Hermez network, including network statistics, transaction data, and other relevant information.
Polygon (MATIC) Price and Market Cap
Throughout the majority of its existence, the MATIC tokens belonging to Polygon, have typically been exchanged for less than five cents each.
Despite a notable increase in value, MATIC has yet to surpass the $3.00 mark. As of February 23, 2024, the going rate for a single MATIC token was approximately $1.39.
Please refer to the chart located above to track the real-time price fluctuations of MATIC and its market cap.
Where to buy Polygon (MATIC)?
To buy the cryptocurrency of Polygon, MATIC, a variety of options are available at your disposal. Currently, Polygon is among the most sought-after cryptocurrencies, boasting a high market cap, which has made it readily accessible on multiple exchanges.
An exchange is a cost-effective method of acquiring cryptocurrencies, enabling you to either store them on the platform or transfer them to a personal cold wallet for enhanced security.
Your choice of platform largely depends on your specific requirements for the coin, whether you intend to use it as a form of payment or hold it as an investment.
Reputable exchanges, such as Coinbase, Binance, Kraken, KuCoin, and Bitstamp, are ideal for this purpose, and our comprehensive reviews of each platform are just a click away.
By utilizing these solutions, you can take control of your assets and enjoy seamless transfers and payments.
It is also recommended that you use a wallet for added security beyond what is typically provided by exchanges alone. The exchanges outlined in this guide offer the option to transfer coins to an internal hot wallet or an external cold wallet (like the Trezor One, for example) of your choosing.
Pros and Cons of Polygon
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| ✅ Ability to process transactions quickly | ❌ Not an autonomous blockchain |
| ✅ Transaction fees are consistently low | ❌ Limited use cases for MATIC |
| ✅ Offers multiple scaling solutions such as side chains and Plasma | ❌ Dependency on Ethereum network |
| ✅ Fully compatible with Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) | ❌ Relatively new platform with limited track record |
| ✅ Over 7,000 blockchain-based projects supported | ❌ Limited adoption compared to major cryptocurrencies |
| ✅ Uses Proof of Stake consensus mechanism for network security | ❌ MATIC not widely accepted as a means of payment |
Bottom line
In summary, Polygon (MATIC) is a Layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum that aims to improve the network's scalability, security, and usability.
With its fast and low-cost transactions, interoperability, and easy-to-use developer tools, Polygon is rapidly gaining popularity among the decentralized finance (DeFi) community and is poised to become a major player in the blockchain industry.
As more and more projects and users flock to the Polygon ecosystem, it will be exciting to see what new innovations and possibilities emerge in the world of decentralized applications.